| Stable release | |
|---|---|
| Repository | JASP Github page |
| Written in | C++, R, JavaScript |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Linux |
| Type | Statistics |
| License | GNU Affero General Public License |
| Website | jasp-stats.org |
This video demonstrates the basic functionality of JASP. The files used in this video can be downloaded at: osf.io/b8mj6 Connect with JASP:Website: https://j. JASP file is a JASP Data. JASP is a free and open-source graphical program for statistical analysis, designed to be easy to use, and familiar to users of SPSS. JASP is installed by downloading and double clicking the.dmg file, and dragging the JASP icon to the Applications folder. This places JASP in your applications folder. It might warn you that it “is a file downloaded from the internet” and it is right, but you can just click through that.
JASP is a free and open-source program for statistical analysis supported by the University of Amsterdam. It is designed to be easy to use, and familiar to users of SPSS. It offers standard analysis procedures in both their classical and Bayesian form.[1][2] JASP generally produces APA style results tables and plots to ease publication. It promotes open science by integration with the Open Science Framework and reproducibility by integrating the analysis settings into the results. The development of JASP is financially supported by several universities and research funds.

JASP offers a fresh way to do statistics. The application is a low-fat alternative to SPSS, and a perfect alternative to R. Bayesian statistics made accessible. The JASP application is written in C, using the Qt toolkit. The analyses themselves are written in either R or C. Alternatives to JASP for Windows, Linux, Mac, Xfce, Web and more. Filter by license to discover only free or Open Source alternatives. Boom boom boom hindi song 2012 mp3 free download. This list contains a total of 21 apps similar to JASP. List updated: 12/3/2020 10:40:00 PM.
Analyses[edit]
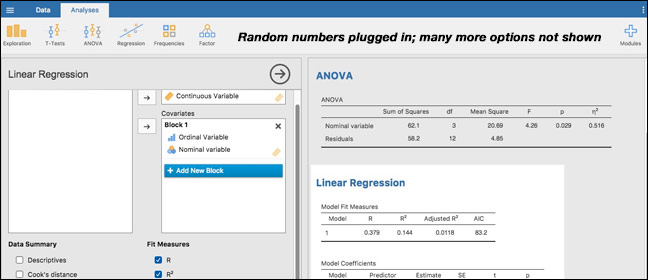
JASP offers frequentist inference and Bayesian inference on the same statistical models. Frequentist inference uses p-values and confidence intervals to control error rates in the limit of infinite perfect replications. Bayesian inference uses credible intervals and Bayes factors[3][4] to estimate credible parameter values and model evidence given the available data and prior knowledge.
The following analyses are available in JASP:
| Analysis | Frequentist | Bayesian |
|---|---|---|
| A/B test | ||
| ANOVA, ANCOVA, Repeated measures ANOVA and MANOVA | ||
| AUDIT (module) | ||
| Bain (module) | ||
| Binomial test | ||
| Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) | ||
| Contingency tables (including Chi-squared test) | ||
| Correlation:[5]Pearson, Spearman, and Kendall | ||
| Equivalence T-Tests: Independent, Paired, One-Sample | ||
| Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) | ||
| Linear regression | ||
| Logistic regression | ||
| Log-linear regression | ||
| Machine Learning | ||
| Mann-Whitney U and Wilcoxon | ||
| Mediation Analysis | ||
| Meta Analysis | ||
| Mixed Models | ||
| Multinomial test | ||
| Network Analysis | ||
| Principal component analysis (PCA) | ||
| Reliability analyses: α, γδ, and ω | ||
| Structural equation modeling (SEM) | ||
| Summary Stats[6] | ||
| T-tests: independent, paired, one-sample | ||
| Visual Modeling: Linear, Mixed, Generalized Linear |
Other features[edit]
- Descriptive statistics and plots.
- Assumption checks for all analyses, including Levene's test, the Shapiro–Wilk test, and Q–Q plot.
- Imports SPSS files and comma-separated files.
- Open Science Framework integration.
- Data filtering: Use either R code or a drag-and-drop GUI to select cases of interest.
- Create columns: Use either R code or a drag-and-drop GUI to create new variables from existing ones.
- Copy tables in LaTeX format.
- PDF export of results.

Modules[edit]
- Summary statistics: Bayesian inference from frequentist summary statistics for t-test, regression, and binomial tests.
- BAIN: Bayesian informative hypotheses evaluation[7] for t-test, ANOVA, ANCOVA and linear regression.
- Network: Network Analysis allows the user to analyze the network structure of variables.
- Meta Analysis: Includes techniques for fixed and random effects analysis, fixed and mixed effects meta-regression, forest and funnel plots, tests for funnel plot asymmetry, trim-and-fill and fail-safe N analysis.
- Machine Learning: Machine Learning module contains 13 analyses for supervised an unsupervised learning:
- Regression
- Boosting Regression
- Random Forest Regression
- Regularized Linear Regression
- Classification
- K-Nearest Neighbors Classification
- Linear Discriminant Classification
- Clustering
- Regression
- SEM: Structural equation modeling.[8]
- JAGS module
- Discover distributions
- Equivalence testing
References[edit]
- ^Wagenmakers EJ, Love J, Marsman M, Jamil T, Ly A, Verhagen J, et al. (February 2018). 'Bayesian inference for psychology. Part II: Example applications with JASP'. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review. 25 (1): 58–76. doi:10.3758/s13423-017-1323-7. PMC5862926. PMID28685272.
- ^Love J, Selker R, Verhagen J, Marsman M, Gronau QF, Jamil T, Smira M, Epskamp S, Wil A, Ly A, Matzke D, Wagenmakers EJ, Morey MD, Rouder JN (2015). 'Software to Sharpen Your Stats'. APS Observer. 28 (3).
- ^Quintana DS, Williams DR (June 2018). 'Bayesian alternatives for common null-hypothesis significance tests in psychiatry: a non-technical guide using JASP'. BMC Psychiatry. 18 (1): 178. doi:10.1186/s12888-018-1761-4. PMC5991426. PMID29879931.
- ^Brydges CR, Gaeta L (December 2019). 'An Introduction to Calculating Bayes Factors in JASP for Speech, Language, and Hearing Research'. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 62 (12): 4523–4533. doi:10.1044/2019_JSLHR-H-19-0183. PMID31830850.
- ^Nuzzo RL (December 2017). 'An Introduction to Bayesian Data Analysis for Correlations'. PM&R. 9 (12): 1278–1282. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2017.11.003. PMID29274678.
- ^Ly A, Raj A, Etz A, Marsman M, Gronau QF, Wagenmakers E (2017-05-30). 'Bayesian Reanalyses from Summary Statistics: A Guide for Academic Consumers'. Open Science Framework.
- ^Gu, Xin; Mulder, Joris; Hoijtink, Herbert (2018). 'Approximated adjusted fractional Bayes factors: A general method for testing informative hypotheses'. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology. 71 (2): 229–261. doi:10.1111/bmsp.12110. ISSN2044-8317. PMID28857129.
- ^Kline, Rex B. (2015-11-03). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, Fourth Edition. Guilford Publications. ISBN9781462523351.
External links[edit]
- jasp-desktop on GitHub
The safest place to get apps for your Mac is the App Store. Apple reviews each app in the App Store before it’s accepted and signs it to ensure that it hasn’t been tampered with or altered. If there’s ever a problem with an app, Apple can quickly remove it from the store.
If you download and install apps from the internet or directly from a developer, macOS continues to protect your Mac. When you install Mac apps, plug-ins, and installer packages from outside the App Store, macOS checks the Developer ID signature to verify that the software is from an identified developer and that it has not been altered. By default, macOS Catalina and later also requires software to be notarized, so you can be confident that the software you run on your Mac doesn't contain known malware. Before opening downloaded software for the first time, macOS requests your approval to make sure you aren’t misled into running software you didn’t expect.
Running software that hasn’t been signed and notarized may expose your computer and personal information to malware that can harm your Mac or compromise your privacy.
View the app security settings on your Mac
By default, the security and privacy preferences of your Mac are set to allow apps from the App Store and identified developers. For additional security, you can chose to allow only apps from the App Store.
In System Preferences, click Security & Privacy, then click General. Click the lock and enter your password to make changes. Select App Store under the header “Allow apps downloaded from.”
Open a developer-signed or notarized app
If your Mac is set to allow apps from the App Store and identified developers, the first time that you launch a new app, your Mac asks if you’re sure you want to open it.
An app that has been notarized by Apple indicates that Apple checked it for malicious software and none was detected:
Prior to macOS Catalina, opening an app that hasn't been notarized shows a yellow warning icon and asks if you're sure you want to open it:
If you see a warning message and can’t install an app
If you have set your Mac to allow apps only from the App Store and you try to install an app from elsewhere, your Mac will say that the app can't be opened because it was not downloaded from the App Store.*
If your Mac is set to allow apps from the App Store and identified developers, and you try to install an app that isn’t signed by an identified developer and—in macOS Catalina and later—notarized by Apple, you also see a warning that the app cannot be opened.
If you see this warning, it means that the app was not notarized, and Apple could not scan the app for known malicious software.
You may want to look for an updated version of the app in the App Store or look for an alternative app.
If macOS detects a malicious app
If macOS detects that an app has malicious content, it will notify you when you try to open it and ask you to move it to the Trash.
How to open an app that hasn’t been notarized or is from an unidentified developer
Running software that hasn’t been signed and notarized may expose your computer and personal information to malware that can harm your Mac or compromise your privacy. If you’re certain that an app you want to install is from a trustworthy source and hasn’t been tampered with, you can temporarily override your Mac security settings to open it.
In macOS Catalina and macOS Mojave, when an app fails to install because it hasn’t been notarized or is from an unidentified developer, it will appear in System Preferences > Security & Privacy, under the General tab. Click Open Anyway to confirm your intent to open or install the app.
The warning prompt reappears, and you can click Open.*
The app is now saved as an exception to your security settings, and you can open it in the future by double-clicking it, just as you can any authorized app.
Jasp Para Macbook
Privacy protections
Sippro v4.0.2 for macos. macOS has been designed to keep users and their data safe while respecting their privacy.

Descargar Jasp Para Mac
Gatekeeper performs online checks to verify if an app contains known malware and whether the developer’s signing certificate is revoked. We have never combined data from these checks with information about Apple users or their devices. We do not use data from these checks to learn what individual users are launching or running on their devices.
Notarization checks if the app contains known malware using an encrypted connection that is resilient to server failures.
These security checks have never included the user’s Apple ID or the identity of their device. To further protect privacy, we have stopped logging IP addresses associated with Developer ID certificate checks, and we will ensure that any collected IP addresses are removed from logs.
In addition, over the the next year we will introduce several changes to our security checks: Dragon age origins hair.
- A new encrypted protocol for Developer ID certificate revocation checks
- Strong protections against server failure
- A new preference for users to opt out of these security protections
*If you're prompted to open Finder: control-click the app in Finder, choose Open from the menu, and then click Open in the dialog that appears. Enter your admin name and password to open the app.